
Predictive Models
from Omics Data
Discover minimal-feature biomarker signatures from high-dimensional omics data using evolutionary algorithms — interpretable, parsimonious, and blazing fast.

Discover minimal-feature biomarker signatures from high-dimensional omics data using evolutionary algorithms — interpretable, parsimonious, and blazing fast.
Four steps from raw omics data to validated, interpretable predictive models.
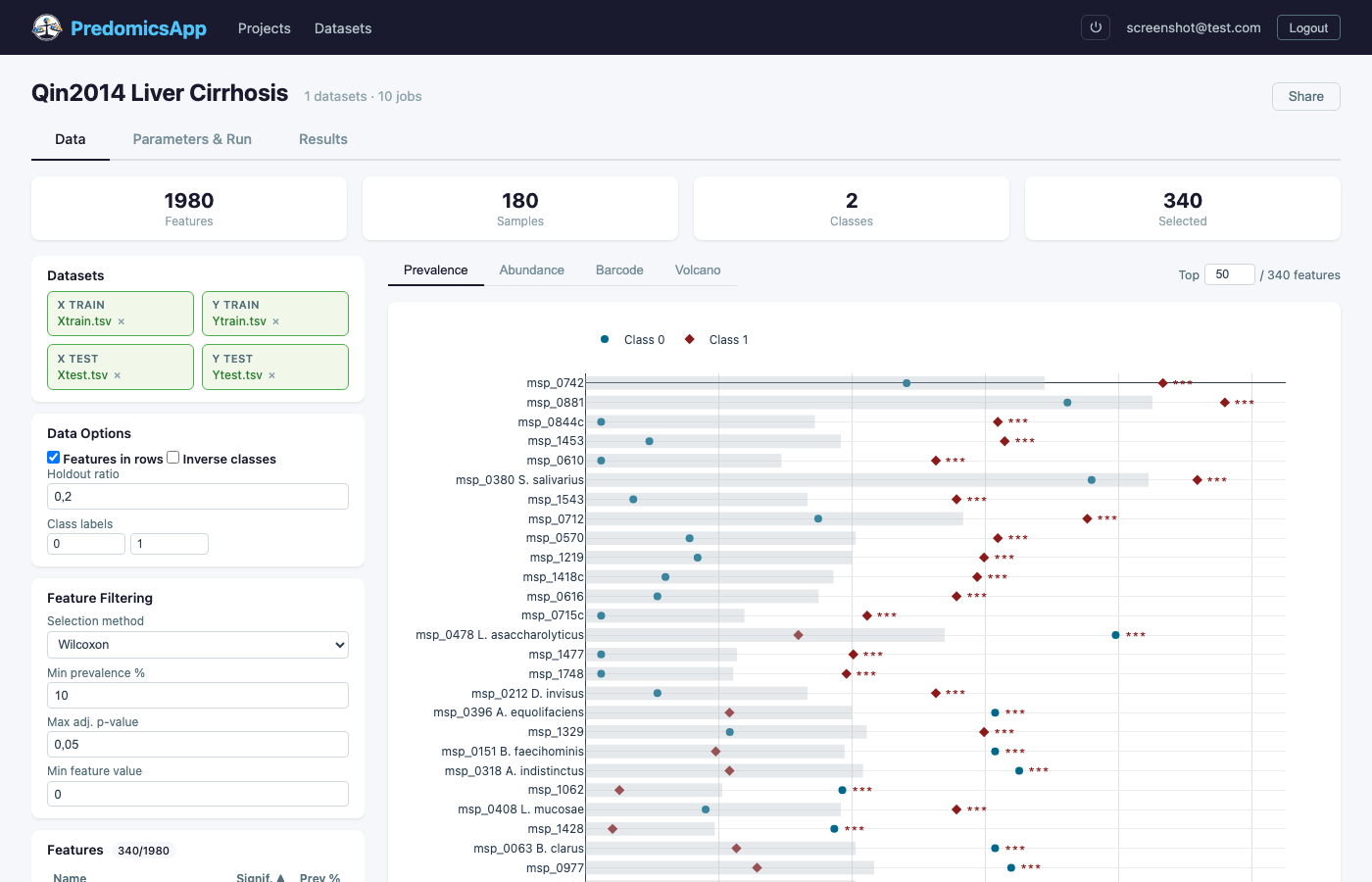
Import TSV/CSV omics matrices with training and optional test sets
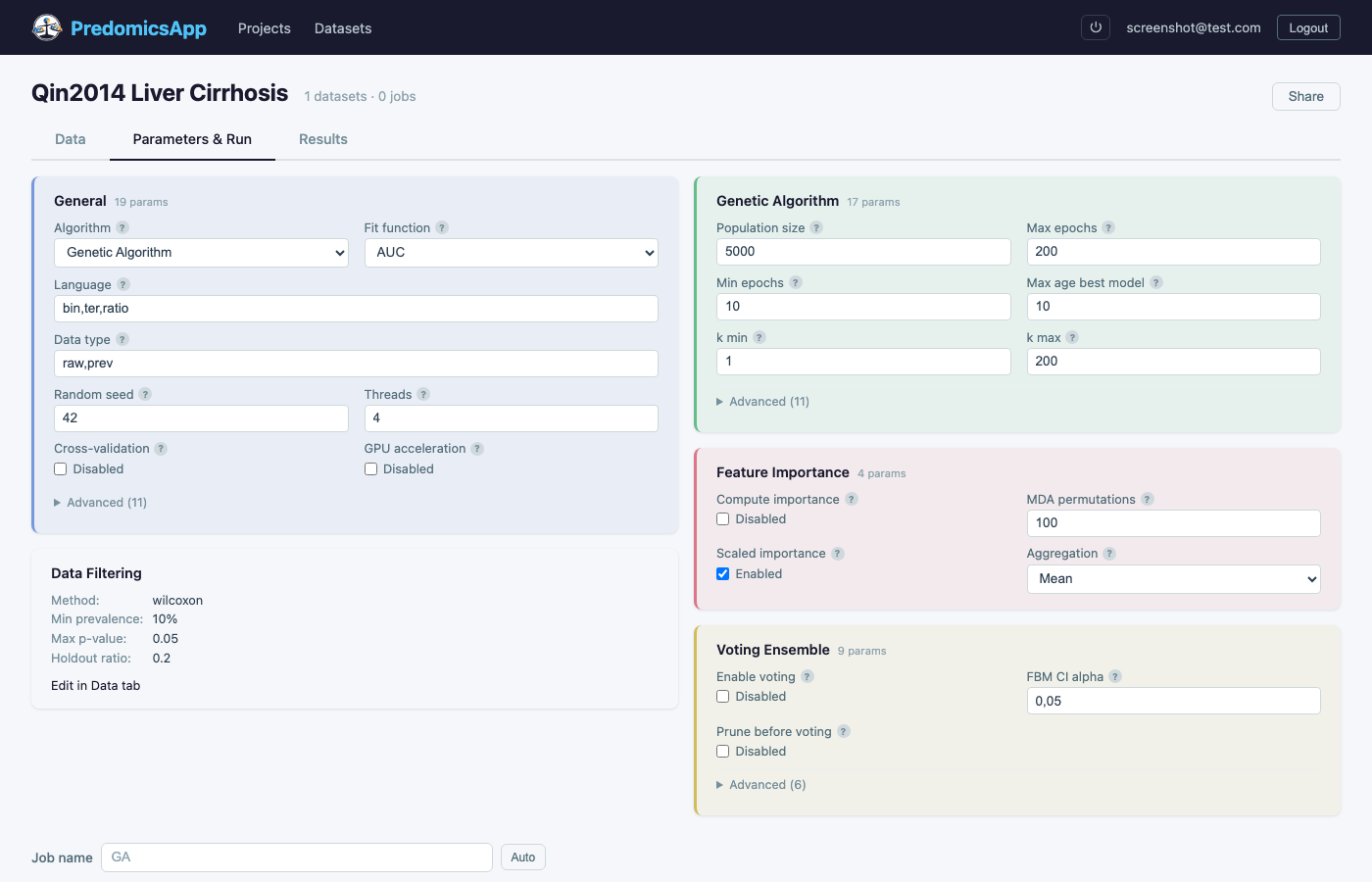
Choose algorithms, model languages, and fine-tune parameters
Launch evolutionary search with real-time progress monitoring
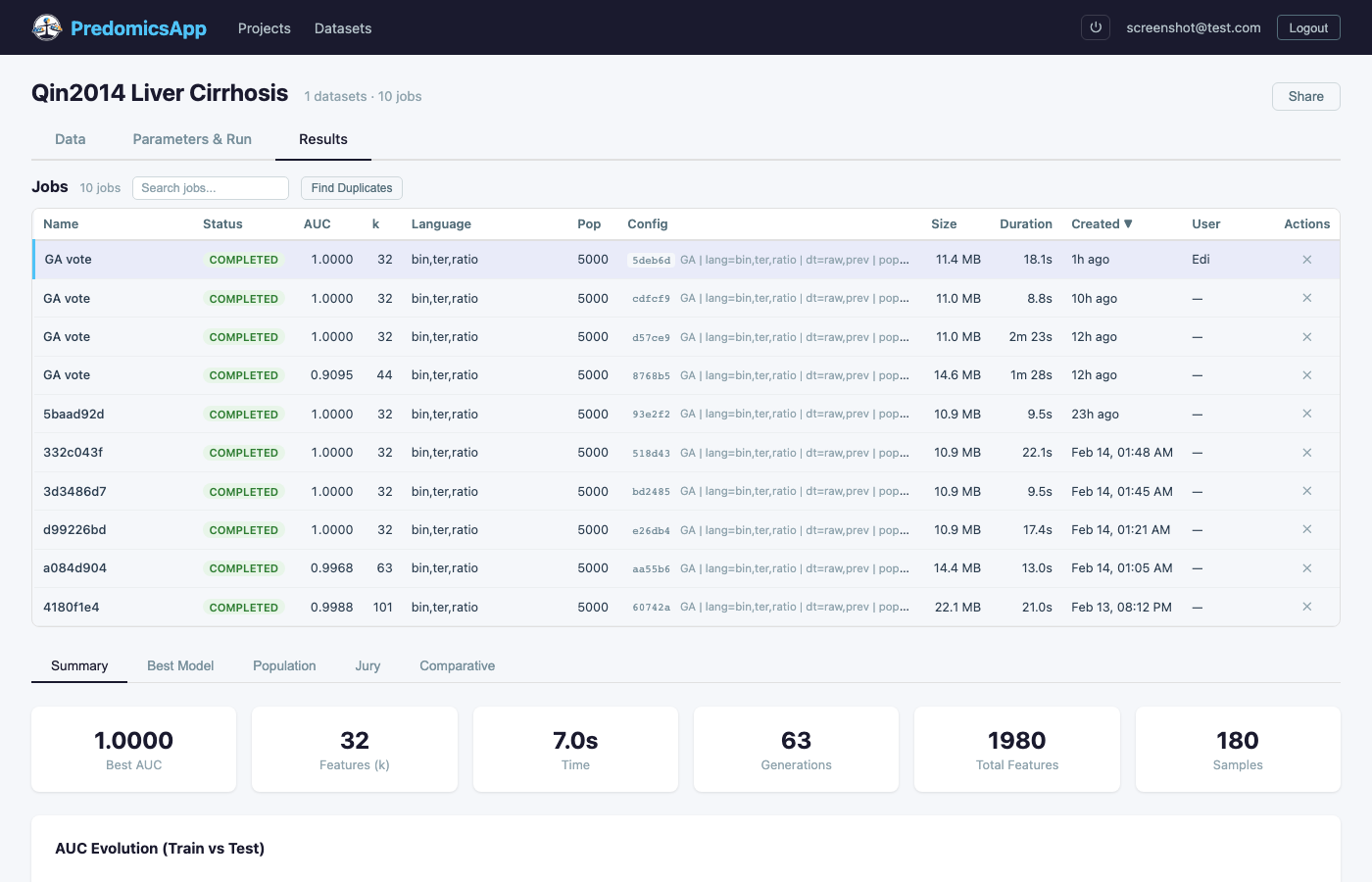
Inspect models, feature importance, jury voting, export reports
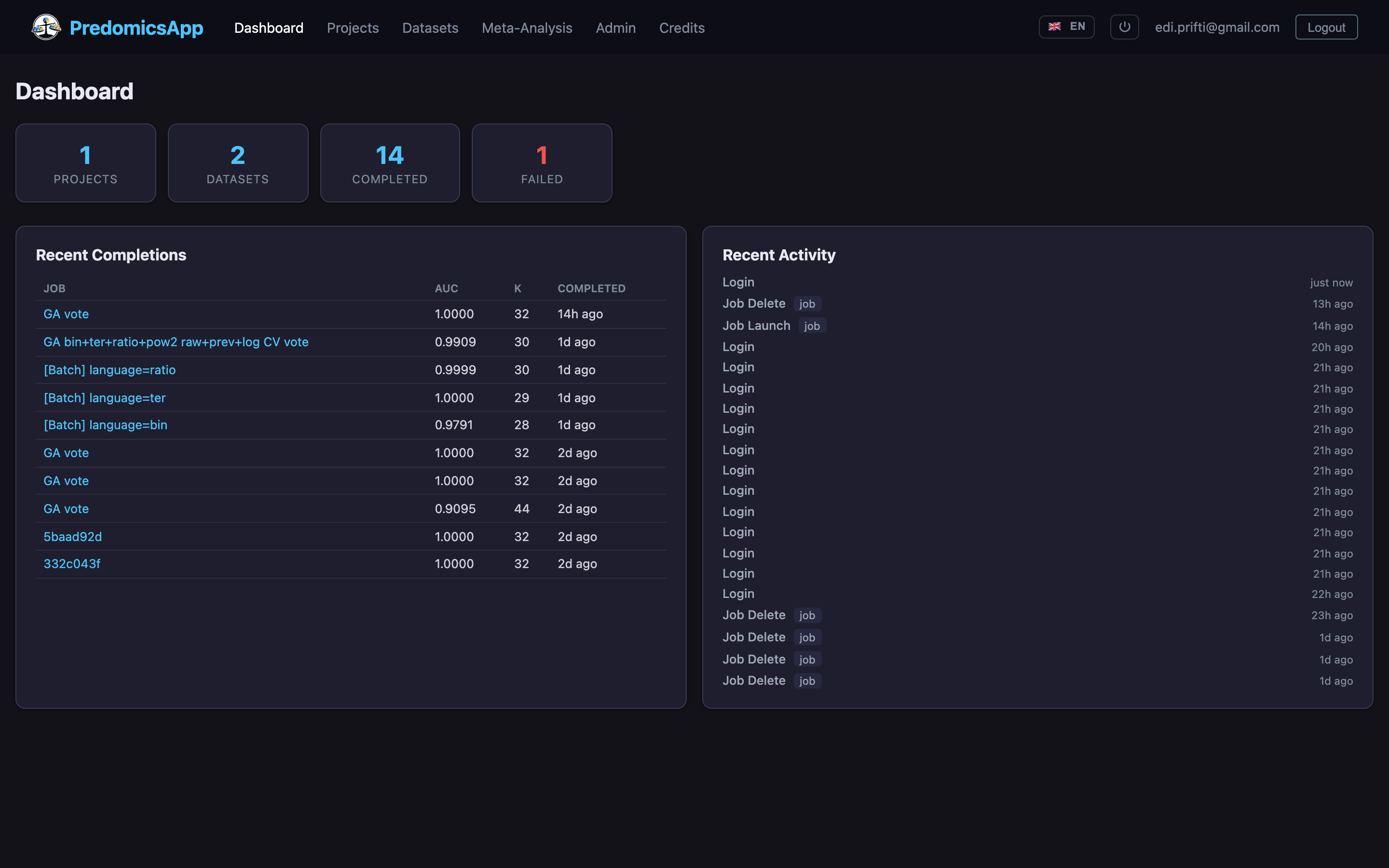
From raw omics matrices to publication-ready models in minutes, with full transparency at every step.
Discovers minimal feature sets (binary, ternary, ratio) that achieve high classification accuracy. Models you can interpret and publish.
Genetic algorithms, beam search, and MCMC heuristics explore the feature space efficiently to find optimal biomarker signatures.
Ensemble of expert models with majority voting, rejection capability, concordance analysis, and per-sample confidence scores.
Prevalence plots, heatmaps, violin plots, SHAP explanations, PCoA, co-presence networks, and 30+ interactive chart types.
Built-in k-fold CV with generation-level tracking. Monitor train vs test AUC, complexity, and fit in real time.
Core engine rewritten in Rust with Python bindings. Up to 1,000x faster than the original R implementation.
A full-stack interface for running analyses, exploring results, and sharing with collaborators.
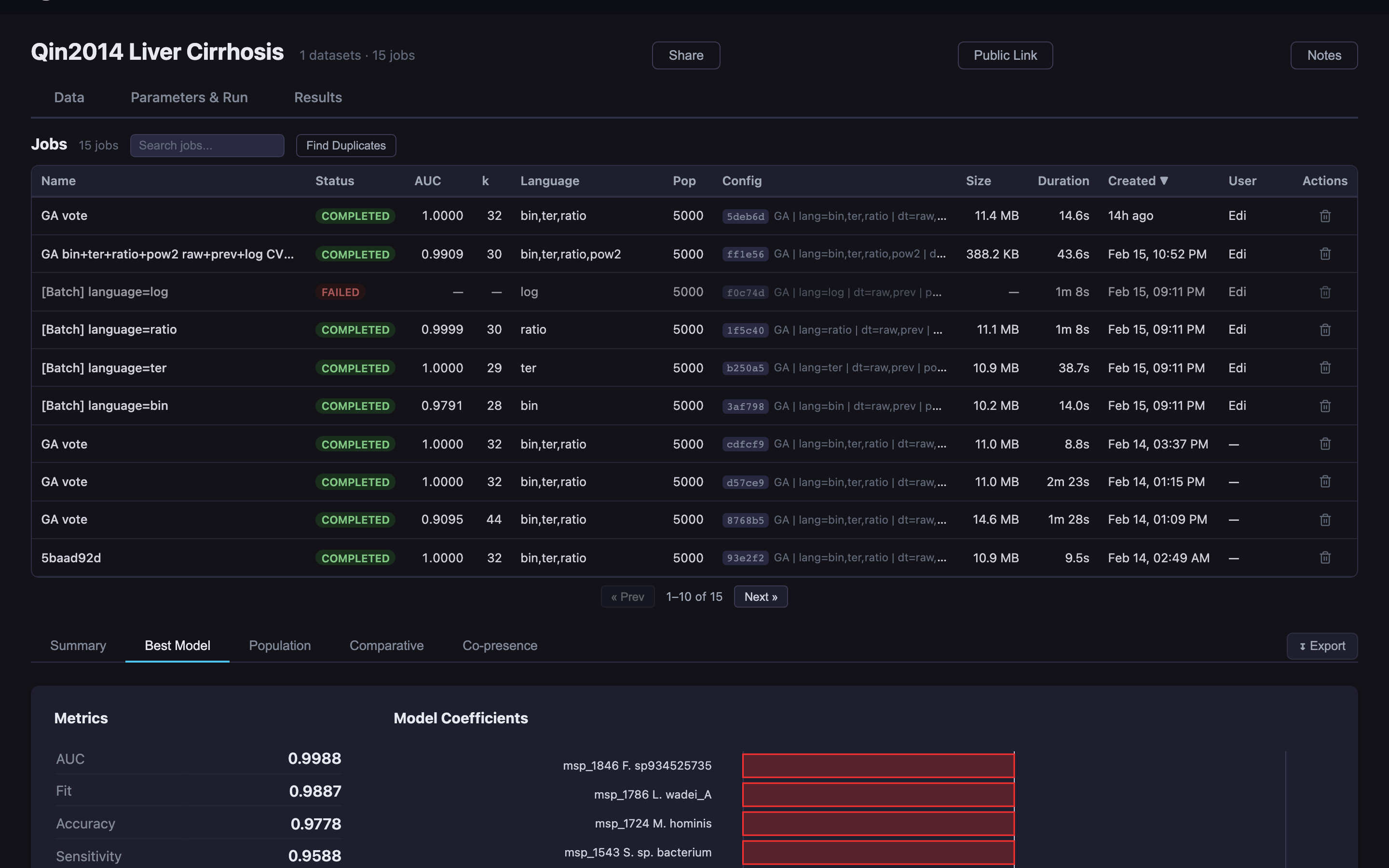

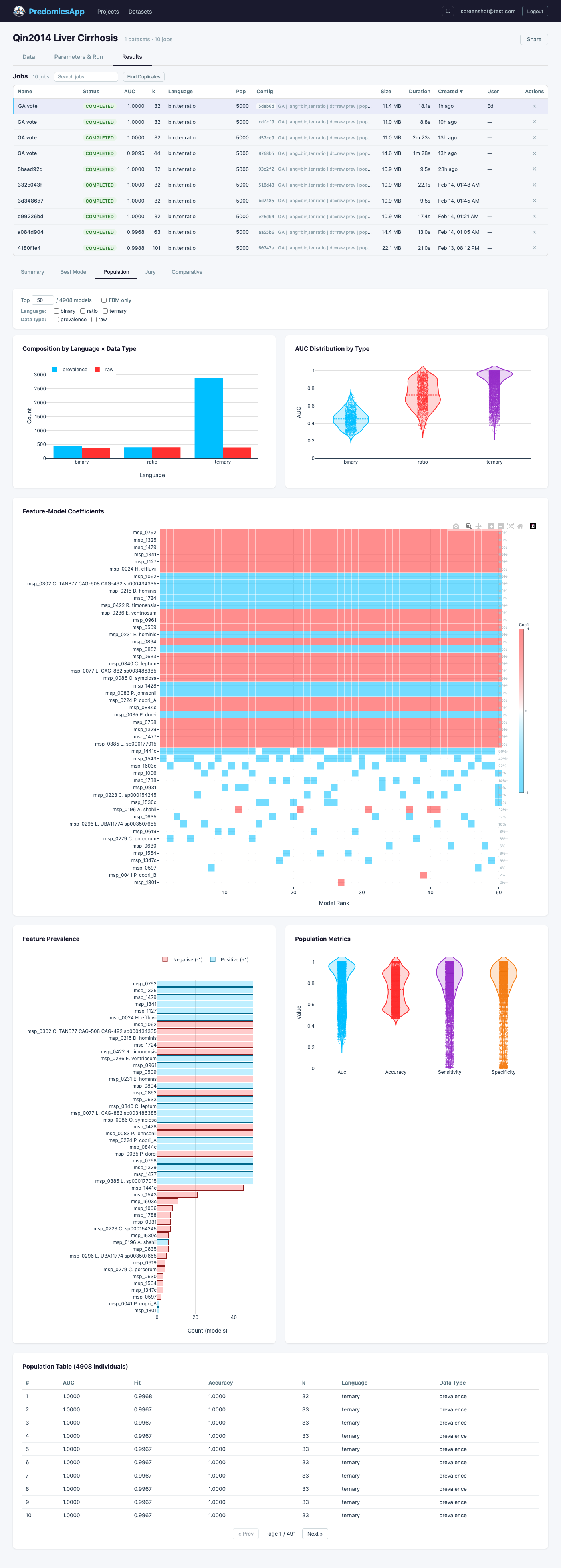
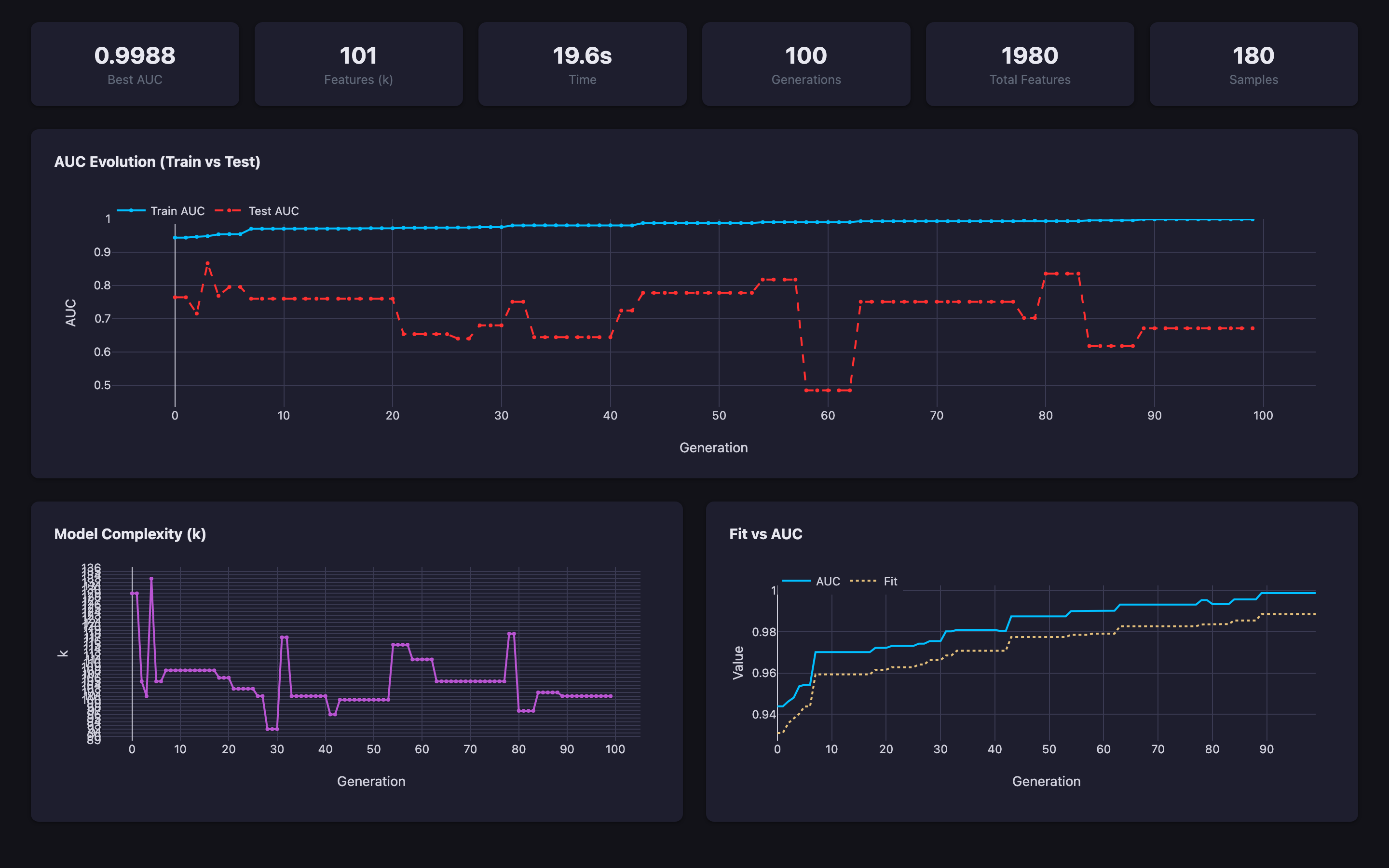
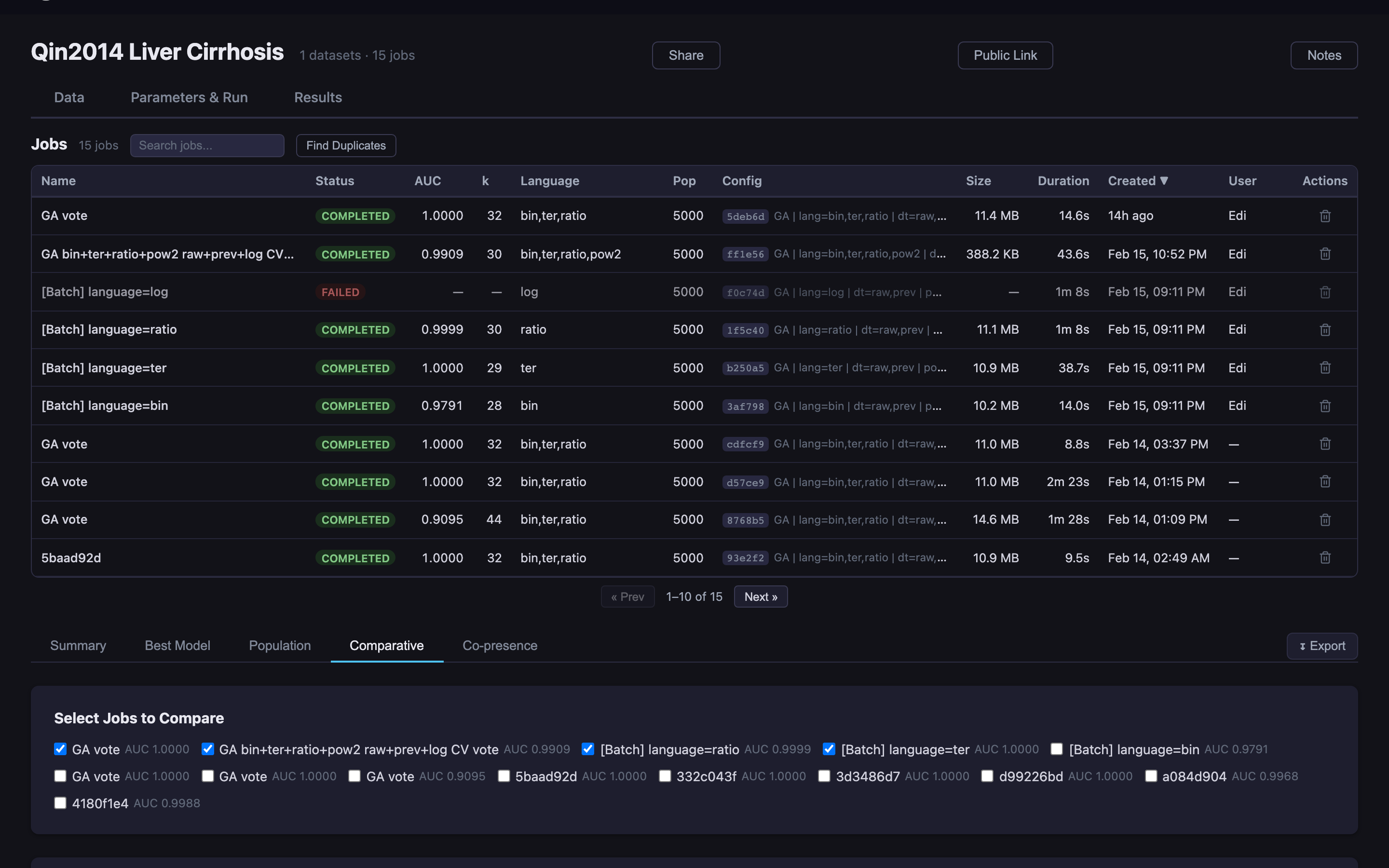
Predomics has been applied to microbiome and multi-omics classification problems across clinical contexts.
Predict liver cirrhosis from gut microbiome composition using metagenomic species abundance profiles.
Classify colorectal cancer status from stool metagenomic data using sparse ternary models.
Predict immunotherapy response from baseline gut microbiome in melanoma patients.
Identify type 2 diabetes biomarkers from metagenome-wide association studies.
Three complementary tools, one unified approach to interpretable omics classification.
High-performance ML engine rewritten in Rust — up to 1,000x faster than the original R package. Python bindings via gpredomicspy for notebooks and scripts.
View Repository →Full-stack web application for running analyses, exploring results with 30+ interactive visualizations, and sharing with collaborators. Deploy anywhere with Docker.
View Repository →R bindings for the gpredomics Rust engine. Bringing the 1,000x Rust speedup to the R ecosystem with a familiar interface.
View Repository →Choose your preferred way to use Predomics.
The researchers, developers, and students behind Predomics.